Concept Analysis for Planning Support:
Example based on our customer AUDI Neckarsulm
Initial Situation
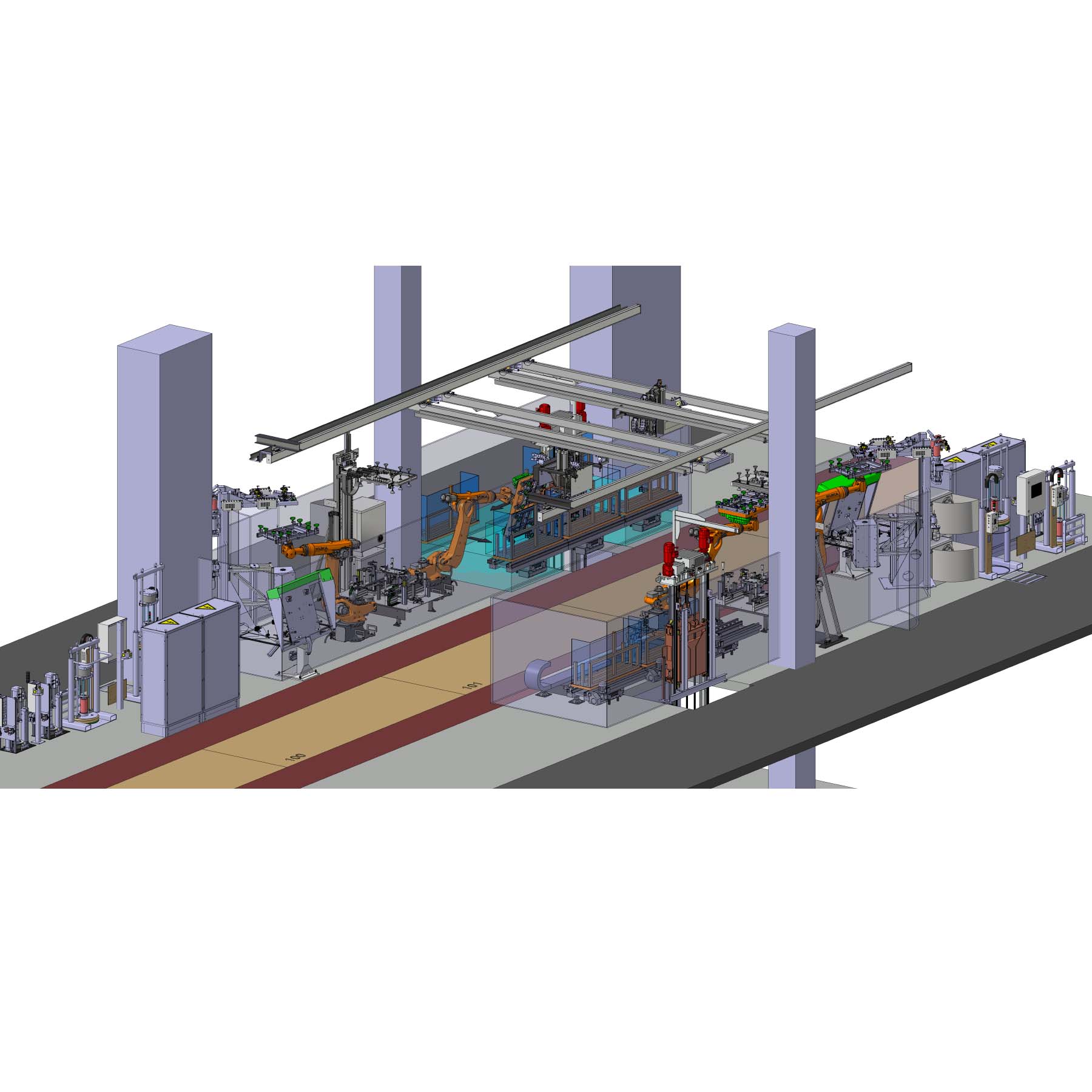
The scope of the study is the conceptual design of two semi-automated windshield bonding systems for processing a complete set of car windows, consisting of a windshield, rear window and a fixed side window (so-called "triangular window") on the left and right side of the vehicle.
The main objectives of the study are the development of technically feasible system layouts, the validation of technical feasibility, the design of system process sequences and the definition of necessary boundary conditions and restrictions at a very early stage of the system project.
The latter refers to the period before the actual tender for implementation (planning support).

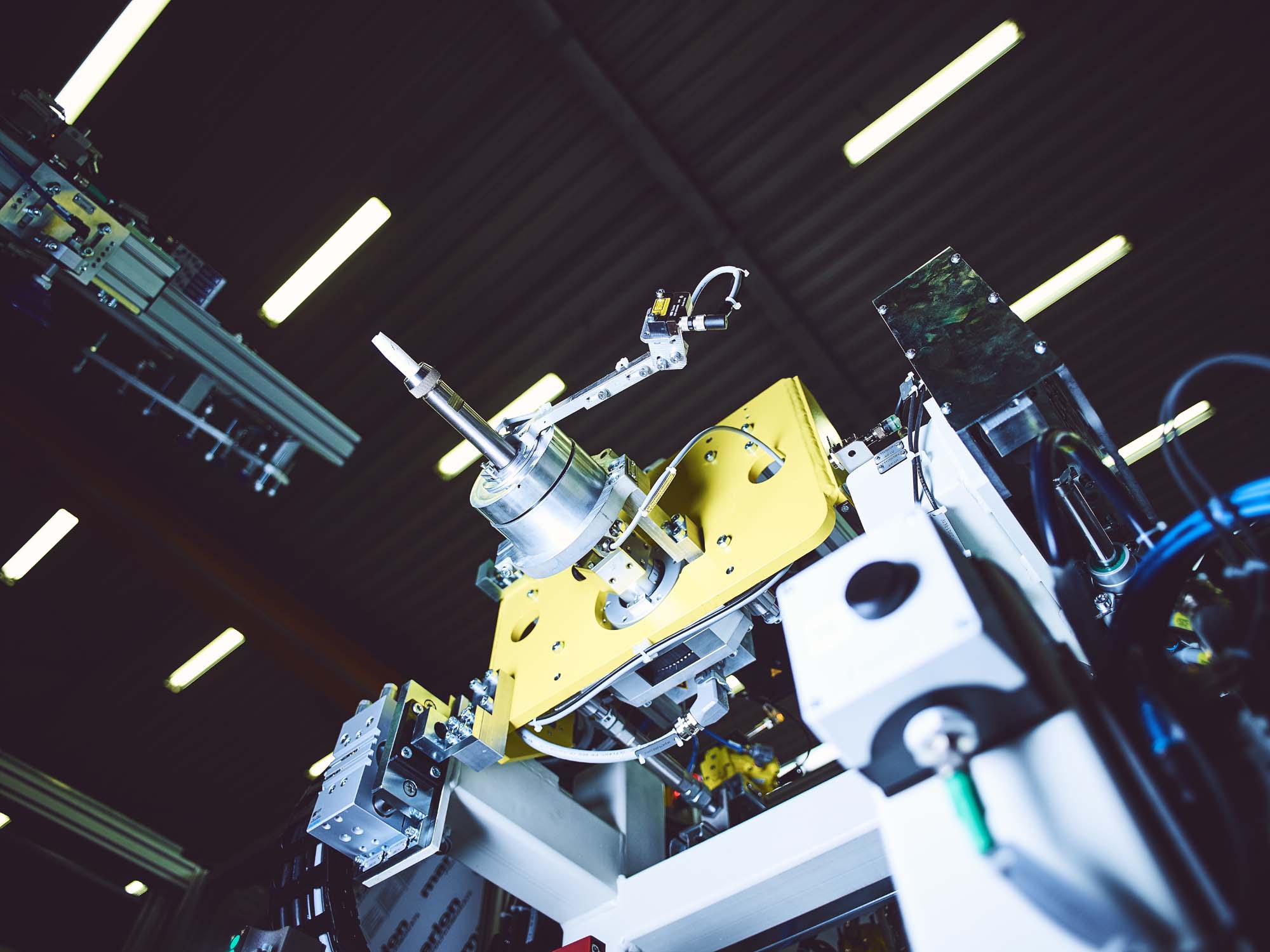
Process sequence
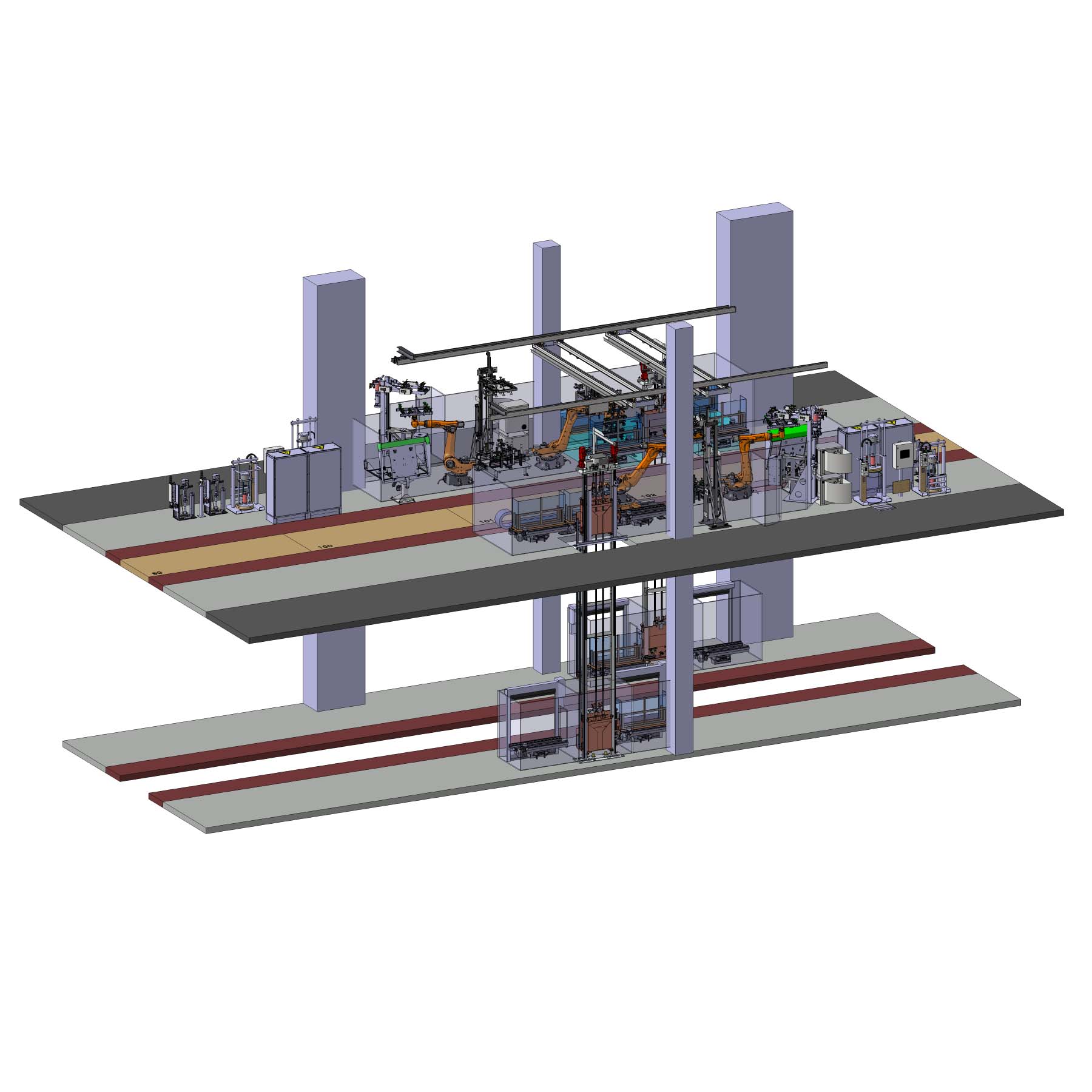
The systems on the first floor are loaded manually, i.e. by the worker, into parts carriers for onward transportation via lifters to the upper floor. The time window for loading should be as large as possible for the employee, which requires a decoupling of worker and lifter via redundant loading stations as well as an optimized parts carrier flow.
On the upper floor, the Glasses are to be automatically removed, precisely positioned, provided with adhesive at stationary adhesive nozzles (application towers) and then offered to the assembly line worker via output stations for collection and installation using a manipulator.
In the series process, both sides of the system share the application of a complete set of glasses.
Challenges in the planning phase
The task is particulary challenging in view of the very tight space conditions, limited cycle time and given structural features such as existing hall columns or ceiling openings to connect the material logistics area on the first floor and the plant area on the upper floor.
Any further intervention in the building structure is not permitted. Furthermore, both systems should be able to stand in for each other in the event of a system failure and take over the workload of the other system (backup).
These requirements have a direct impact on the design of the robot cells as well as on the system processes. Different spatial conditions requre separate approaches for both sides of the system to ensure equivalent functionality.